Nonwoven Fabric Manufacturing Tension Control
Tools that improve quality and increase efficiency in nonwoven production processes.
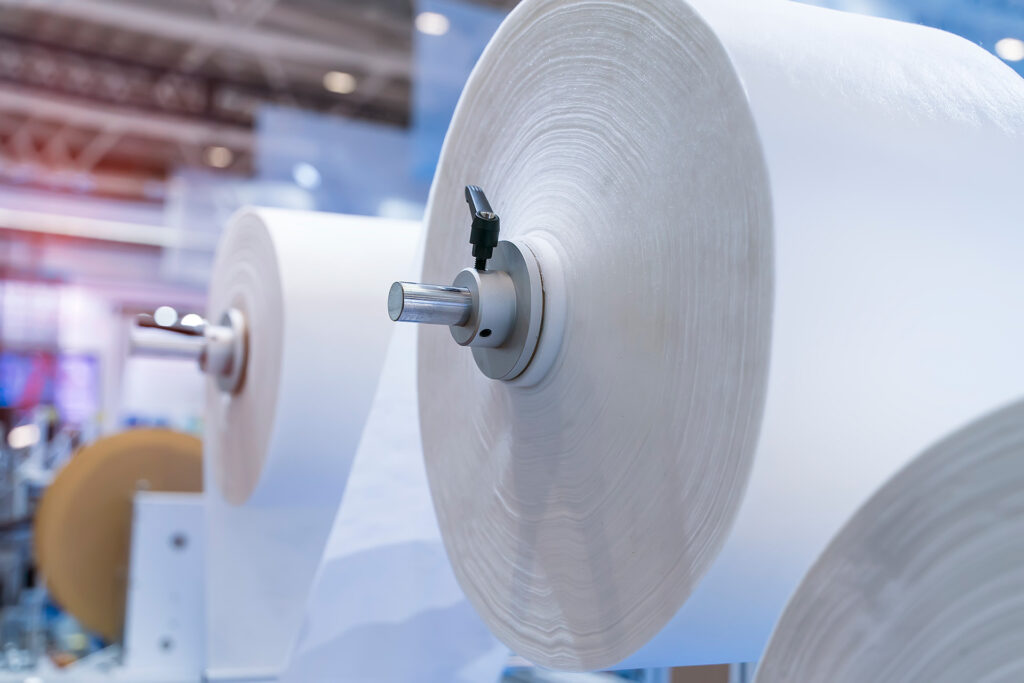

Nonwoven fabrics, engineered through processes that bond or interlock fibers without weaving or knitting, are integral to industries ranging from healthcare to construction. The most common types of nonwoven fabrics are spunbond, meltblown, spunlace, airlaid, and wetlaid. Each of these fabric types have unique tension requirements based on their inherent structural properties.
WHY TENSION CONTROL MATTERS IN NONWOVEN MANUFACTURING
Nonwoven fabric production involves handling continuous webs of fibers or filaments, often at high speeds and with varying material properties. Inconsistent tension can lead to defects such as wrinkles, tears, or uneven thickness, which compromise product performance and increase scrap rates.
Proper tension control ensures:
Uniform Product Quality: Consistent tension maintains even fiber distribution and bonding, critical for fabric strength and functionality.
Reduced Waste: Precise tension minimizes material stretch, breakage, or misalignment, reducing costly scrap.
Increased Efficiency: Stable tension allows for higher production speeds and less downtime due to web breaks or adjustments.
Enhanced Process Reliability: Automated tension control reduces operator intervention, ensuring repeatable results.
Versatility: Controlled tension enables manufacturers to process a wider range of materials on a single line.
Dover Flexo Electronics, a leader in tension control technology for over 50 years, provides tailored solutions that address these needs, delivering measurable improvements in nonwoven fabric production. Below, we examine the role of tension control in manufacturing of the Top Five nonwoven fabric types:
1. SPUNBOND NONWOVENS
Spunbond nonwovens are produced by extruding continuous filaments, typically polypropylene (PP), which are laid into a web and bonded thermally or mechanically. These fabrics are strong, durable, and widely used in diapers, geotextiles, and medical gowns.
Tension Control Benefits:
Uniform Filament Distribution: Consistent tension during web formation prevents filament clumping or gaps, ensuring uniform fabric density.
Preventing Stretching: Over-tension can elongate filaments, weakening the fabric. Controlled tension maintains structural integrity.
Smooth Winding: Proper tension during winding prevents roll defects like telescoping or soft spots, critical for downstream converting.
2. MELTBLOWN NONWOVENS
Meltblown nonwovens are made by extruding molten polymer into fine fibers, which are blown into a web and bonded. These fabrics, known for their fine fiber structure, are critical for filtration media in masks and air filters.
Tension Control Benefits:
Preserving Fiber Fineness: Low, stable tension is essential to avoid stretching or tearing the delicate meltblown web, preserving its filtration efficiency.
Consistent Layering: In SMS (spunbond-meltblown-spunbond) composites, precise tension ensures proper alignment and adhesion of layers.
Minimizing Web Breaks: Meltblown webs are fragile; controlled tension reduces breaks during processing and winding.
3. SPUNLACE NONWOVENS
Spunlace nonwovens are created through hydroentanglement, where high-pressure water jets entangle fibers into a strong, soft fabric. They are used in wipes, medical drapes, and apparel.
Tension Control Benefits:
Stable Web Formation: Consistent tension during hydroentanglement prevents web distortion, ensuring uniform entanglement and fabric strength.
Preventing Misalignment: Proper tension aligns fibers correctly, reducing defects like uneven texture or weak spots.
High-Speed Processing: Controlled tension supports faster transit speeds without compromising quality.
4. AIRLAID NONWOVENS
Airlaid nonwovens are formed by dispersing fibers (often wood pulp or synthetic blends) in air and bonding them thermally or with resin. They are used in absorbent products like feminine hygiene pads and tablecloths.
Tension Control Benefits:
Uniform Thickness: Consistent tension ensures even fiber deposition, critical for absorbency and product performance.
Preventing Wrinkles: Controlled tension during bonding prevents web buckling or folding, reducing defects.
Low-Tension Handling: Airlaid webs are often tacky or fragile; precise tension minimizes stretching or tearing.
5. WETLAID NONWOVENS
Wetlaid nonwovens are produced by suspending fibers (e.g., fiberglass, PET, or cellulose) in water, forming a web on a screen, and bonding it. They are used in roofing mats, battery separators, and specialty papers.
Tension Control Benefits:
Consistent Web Formation: Stable tension during web transfer from the screen prevents fiber clumping or gaps.
Preventing Tears: Wetlaid webs are heavy and wet; controlled tension reduces tearing during drying and bonding.
Uniform Bonding: Proper tension ensures even resin or thermal bonding, critical for strength and durability.
CONCLUSION
Tension control is a cornerstone of high-quality nonwoven fabric production, directly impacting product performance, waste reduction, and operational efficiency. For spunbond, meltblown, spunlace, airlaid, and wetlaid nonwovens, precise tension management ensures uniform webs, fewer defects, and faster production speeds.
Dover Flexo Electronics industry-leading solutions, including the Tension Roll® Transducer, SteadyWeb 6™ Controller, and Model C Series Transducers, empower manufacturers to optimize these processes, delivering measurable improvements in quality and profitability.
By investing in DFE’s tension control technology, nonwoven producers also leverage the experience of DFE’s team of applications engineers, dedicated to achieving high-performance results tailored to the customer’s specific manufacturing process.
A typical DFE tension control solution includes a closed-loop controller (e.g., SteadyWeb 6™), a load cell (e.g., Tension Roll® or Model C transducer), and a brake or motor drive system. These components work together to deliver precise, repeatable tension, complementing the unique properties of nonwoven materials.
For manufacturers integrating with PLCs, DFE offers tension amplifiers with analog or ethernet connectivity, such as the TA1 and TA500, enabling seamless data collection and process monitoring.
Do you have a similar tension application that you would like to discuss?
Complete the form below and a DFE Applications Engineer will contact you shortly.
DFE does not share information with 3rd party advertisers.
RESOURCES
Nonwoven Fabric Manufacturing Tension Control (PDF)






